Why is Physical Activity Important?
Physical activity is essential for overall health and wellbeing. Achieving the recommended amount of exercise a week can reduce the risk of diseases, such as coronary heart disease, strokes and type 2 diabetes, as well as helping to maintain a healthy weight.
Physical activity can improve sleep by reducing the length of time it takes to fall asleep, reduce daytime tiredness and increase sleep duration. When you exercise mood boosting chemicals are released in the brain, which can help to reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety.
How much Physical Activity do I need?
Anyone between the ages of 5-18 years old should get an average of at least 60 minutes per day of medium to high intensity physical activity across the week.
This can include all kinds of physical movement, for example:
- swimming
- dancing
- cycling
- skateboarding
- sports such as football, tennis, hockey and rugby
- physical education
- active travel such as walking or biking to school
- after-school activities.
Young people should also aim for muscle and bone strengthening activities on at least three days a week.
This can include:
- jumping
- dancing
- skipping
- yoga
- sports that require quick changes in direction such as basketball or football and racquet sports such as tennis or badminton.
Try to do a variety of types and intensities of physical activity across the week to develop movement skills, muscular fitness, cardiovascular fitness, bone strength and reduce overuse injuries from repetitive sports.
It is also encouraged to try to reduce the amount of time spent sitting down and instead move more even light physical activity such as standing, walking, playing with friends or a pet.
For young people aged over 18 years, guidelines change to 150 minutes of medium level physical activity a week or 75 minutes of high level physical activity a week or a combination of both spread over a week. It is also advised to do muscle and bone strengthening activities on at least two days a week, as well as also trying to break up long periods of sitting with light physical activity.

Why is Strength Training Important?
Strength training is usually associated with spending hours in the gym lifting heavy weights, but this should not be the case.
Strength training is any activity that challenges and builds muscles, this can include everyday activities, such as carrying a heavy school bag, climbing the stairs, swimming or riding a bike, especially uphill. It can be a variety of activities, the important part is gradually increasing the demand on your muscles.
Strength training is a great form of exercise for improving overall health. The most obvious benefit of strength training is stronger muscles, which is important because as you age you will gradually lose muscle, normally from age 40.
Including strength training as a part of routine now will help you later in life when you are much older. It will help reduce the risk of falls, improve flexibility and mobility to allow you to carry out daily tasks even as you age, as well as improve bone strength to reduce the risk of fractures and breaks. Strength training also helps reduce the risk of injuries and improves recovery, so especially important to include in routine if you play sport.
Examples include bodyweight or weighted exercises, e.g squats, push up, lunges, plank, yoga, Pilates, hill walking, cycling
Top tips to be more active
- Stand instead of sitting when you can e.g. on the bus/train or even get off a stop or two early and walk the rest of your journey
- Take the stairs instead of a lift
- Find activities that you enjoy – you are much more likely to stick to something if you enjoy it and want to do it more
- Keep track of your progress e.g. with steps, with distance or with duration – setting a daily target and hitting these goals is very encouraging and will mean you more likely to stick to them
- Ask a friend or family member to join you, whether that is going for a walk, trying a new activity or sport together or renting a court – having someone there that is like minded and has the same goals as you can help encourage you to keep going
- Creating a habit – set a reminder on your phone to get up and move every 30 minutes or once you finish an episode of a show take a break, get up and move, even if that is just stretching or going to get a drink
- Reward yourself – set targets and once you hit these targets reward yourself whether that is a new activewear set, watching an episode of your favourite tv show or going for a nice meal
- Workout at home – this can be much easier if you are short of time or find a gym environment intimidating. You can use household items such as heavy water bottles or milk cartons as weights and follow at home workouts from apps such as YouTube – start with beginner workouts and build up from there.
Why not try a new sport?
It’s easy to get stuck in a routine with the same sports or workouts — or not even realise just how many different ways there are to get active — but there’s a whole world of fun and unique physical activities out there! Have you heard of these ones?

Footgolf
A mix of both football and golf. Individuals will kick a football into oversized golf holes in as few kicks as possible.

Pickleball
A mix of tennis, badminton and ping-pong. This is usually played in singles or in pairs. Hard paddles and a light plastic ball with holes in it (a wiffle ball) are used.
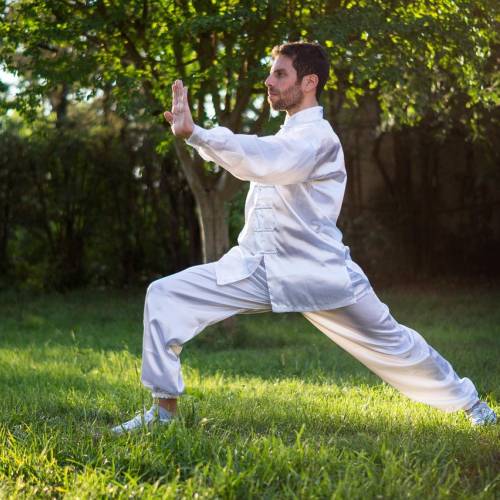

Tai Chi
Chinese martial art that involves deep slow movements, breathwork and meditation. This helps to improve relaxation and is beneficial for improving both physical health and mental health.
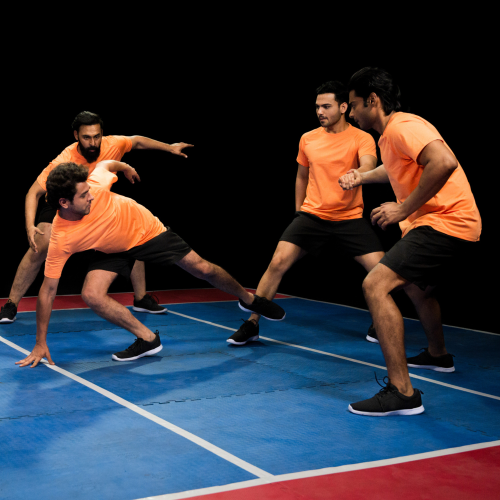

Kabaddi
A team game were players take turns crossing onto the other team’s side, repeating “kabaddi, kabaddi”. To score points players must tag as many opponents as possible without being caught all whilst holding their breath before returning to their side.

Tchoukball
A mix of handball, volleyball, and basketball. This is a non-contact game that is played on a court with 2 trampoline-like frames at opposite ends of the court. The aim of the game is to throw the ball into the opposing team’s frame and prevent them from catching it.
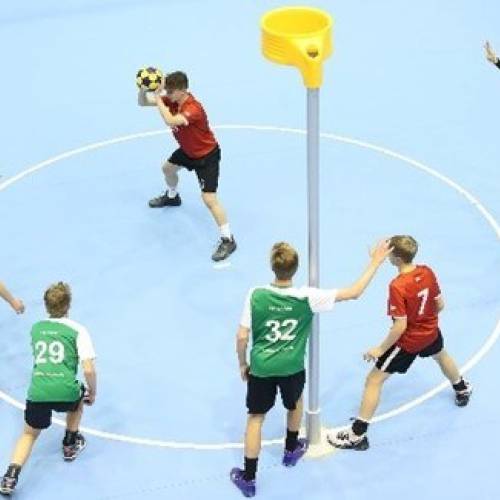

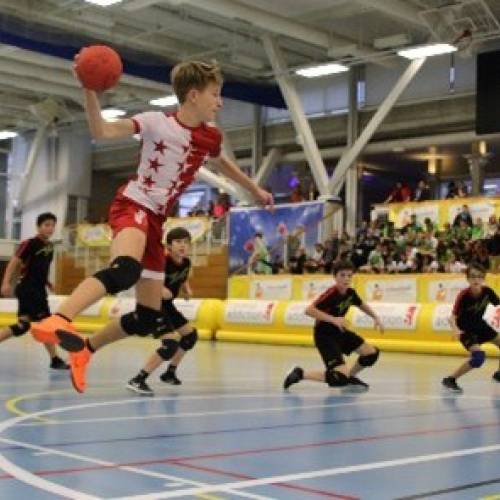
Korfball
A mix of both basketball and netball. There are 2 teams, each consisting of 4 females and 4 males. The aim of the game is to shoot a ball into the korf basket which is set in the end of the playing area enabling players to shoot from 360 degrees. There are 2 player zones: attack and defence. Each zone will have 2 female players and 2 male players. Players are only allowed to oppose members of their own sex.
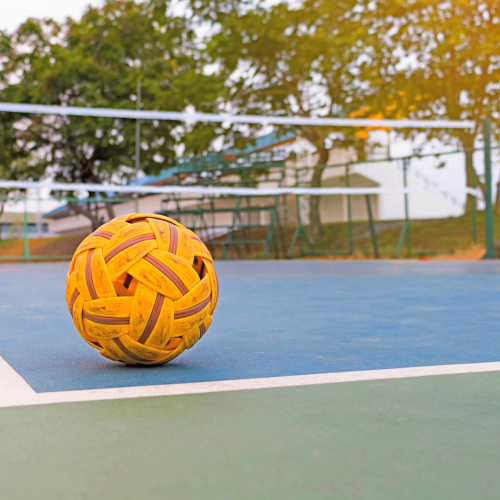

Sepak Takraw
This is a game similar to volleyball that originated in Southeast Asia. Players compete against their opposition on a volleyball like court. Players are only allowed to use their feet, head, knees and chest to touch the ball.
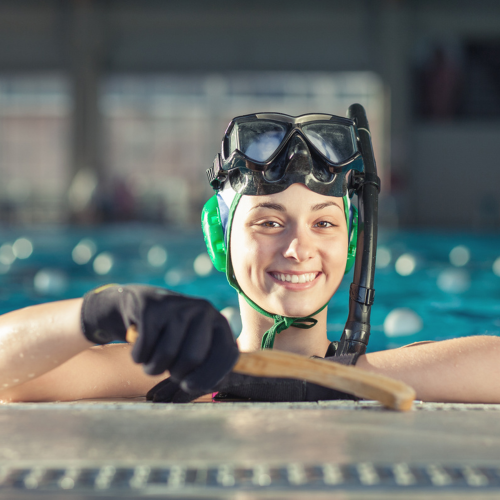

Octopush
This involves both hockey and swimming. The aim is to successfully hit the puck into the opponent’s goal. The game is completely underwater and all players should remain underwater until a goal has been scored.
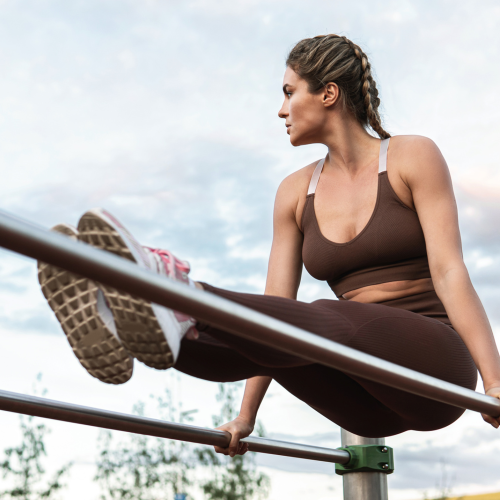

Calisthenics
Calisthenics is a form of strength training that uses your own body weight as resistance in order to build strength, endurance and flexibility. It includes basic movements such as planks, squats, press ups and pull ups, as well as more advanced movements, like muscle ups, handstands and human flag.
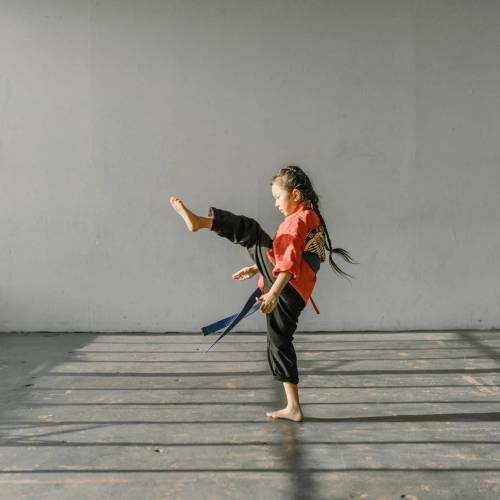

Muay Thai
Also known as Thai boxing, is a martial art and combat sport. It involves striking, which includes powerful punches, kicks and elbow strikes, and clinch work, which is close range grappling. Muay Thai requires fighters to undergo high intensity physical conditioning training to improve cardiovascular fitness.

